Scientists discover 4 new Nazca Geoglyphs using AI deep learning
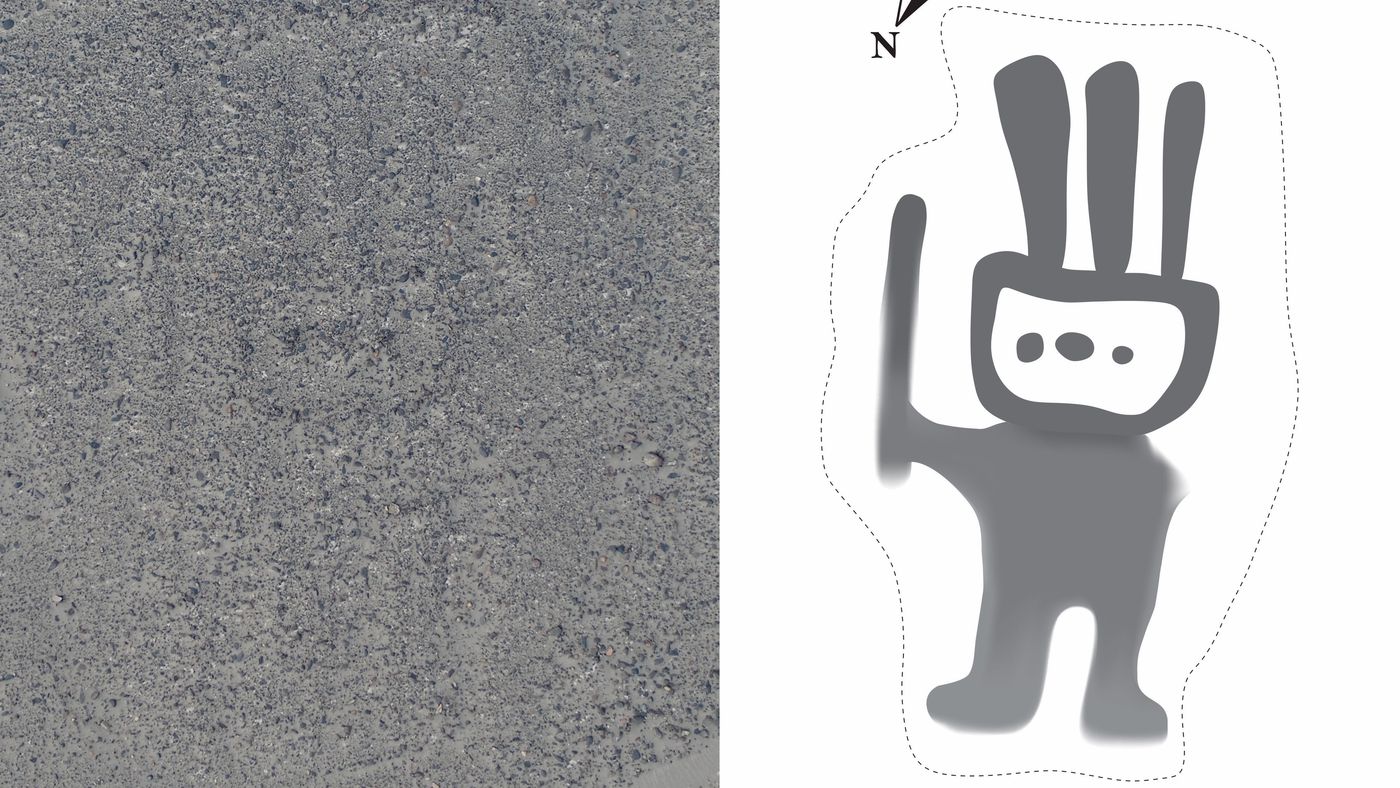
Scientists from Japan used AI deep learning to discover new geoglyphs in the Arid Peruvian coastal plain, in the northern part of Peru’s Nazca Pampa.
The research has been ongoing since 2004 by a team from Yamagata University, led by Professor Makato Sakai. Yamagata University has been conducting geoglyph distribution surveys using satellite imagery, aerial photography, airborne scanning LiDAR, and drone photography to investigate the vast area of the Nazca Pampa covering more than 390 km2.
The Nazca Lines are thought to have been made over centuries, starting around 100 BC by the Nazca people of modern-day Peru. They were first studied in detail in the 1940s, and by the time they were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994, around 30 were identified. They’re remarkably well-preserved considering their age, helped by the desert’s dry climate and winds that sweep away the sand but are being obscured by floods and human activity.
Archaeologists discovered 142 new designs in the desert over the course of ten years by manually identifying them using aerial photography and on-site surveying. Then, in collaboration with IBM Japan researchers, they used machine learning to search the data for designs that had been missed in previous studies.
More:
https://arkeonews.net/scientists-discover-4-new-nazca-geoglyphs-using-ai-deep-learning/
