Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
Editorials & Other Articles
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Environment & Energy
Related: About this forumReuters: US power system becomes more fossil-dependent than China's
https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/us-power-system-becomes-more-fossil-dependent-than-chinas-maguire-2024-10-25/US power system becomes more fossil-dependent than China's
By Gavin Maguire
October 25, 2024 1:13 PM EDT
Commentary
By Gavin Maguire
LITTLETON, Colorado, Oct 25 (Reuters) - Utilities in the United States have relied on fossil fuels to generate a larger share of electricity than their counterparts in China since June, seriously undermining U.S. claims to be a leader in energy transition efforts.
U.S. utilities have relied on fossil fuels to generate an average of 62.4% of total electricity production for the past four months, according to data from energy think tank Ember.
That fossil fuel share exceeds the 60.5% over the same period in China, the world's largest power producer and polluter.

China vs USA share of electricity generation from clean & fossil fuels
The high U.S. fossil dependence came during the summer when domestic power demand is highest due to air conditioner use, while China's relatively lower fossil reliance has occurred during a protracted economic slowdown.
…
By Gavin Maguire
October 25, 2024 1:13 PM EDT
Commentary
By Gavin Maguire
LITTLETON, Colorado, Oct 25 (Reuters) - Utilities in the United States have relied on fossil fuels to generate a larger share of electricity than their counterparts in China since June, seriously undermining U.S. claims to be a leader in energy transition efforts.
U.S. utilities have relied on fossil fuels to generate an average of 62.4% of total electricity production for the past four months, according to data from energy think tank Ember.
That fossil fuel share exceeds the 60.5% over the same period in China, the world's largest power producer and polluter.

China vs USA share of electricity generation from clean & fossil fuels
The high U.S. fossil dependence came during the summer when domestic power demand is highest due to air conditioner use, while China's relatively lower fossil reliance has occurred during a protracted economic slowdown.
…
6 replies
 = new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
= new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
Reuters: US power system becomes more fossil-dependent than China's (Original Post)
OKIsItJustMe
Oct 2024
OP
NPR: Natural gas can rival coal's climate-warming potential when leaks are counted
OKIsItJustMe
Oct 2024
#5
China is rapidly taking global renewable capacity expansion to another level
OKIsItJustMe
Oct 2024
#6
Basso8vb
(1,230 posts)1. Everything coming from China is a lie.
Everything.
Is the land of shortcuts and fakery.
OKIsItJustMe
(21,734 posts)2. Yeah, so we don't have to do anything
God knows, all of the products we’re importing are fake. You know… consumer electronics, solar panels, wind turbines… They’re probably all fake.
Caribbeans
(1,285 posts)3. Projection
Everyone should ALWAYS believe US "officials"
FBaggins
(28,695 posts)4. A deceptive statistic in at least two wayss
Lumps all fossil fuels together when the US has shifted fairly dramatically away from coal and into natural gas
Proportion of energy generation isn't really relevant when total fossil fuel consumption is up dramatically
Combine the two and US coal consumption in the last 25 years or so has been cut in half while China's coal consumption as tripled.
OKIsItJustMe
(21,734 posts)5. NPR: Natural gas can rival coal's climate-warming potential when leaks are counted
https://www.npr.org/2023/07/14/1187648553/natural-gas-can-rival-coals-climate-warming-potential-when-leaks-are-counted
Natural gas can rival coal's climate-warming potential when leaks are counted
JULY 14, 20232:21 PM ET

The natural gas production and supply system leaks the powerful greenhouse gas methane during drilling, fracking, processing and transport.
Meredith Miotke for NPR
Natural gas has long been considered a more climate-friendly alternative to coal, as gas-fired power plants generally release less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than their coal-fired counterparts. But a new study finds that when the full impact of the industry is taken into account, natural gas could contribute as much as coal to climate change.
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. A new peer-reviewed analysis in the journal Environmental Research Letters finds that when even small amounts of methane escape from natural gas wells, production facilities and pipelines, it can drive up the industry's emissions to equal the effects of coal.
Recent studies have found much higher rates of leakage from natural gas infrastructure than previously known. Researchers wanted to understand the impact of those leaks.
"This analysis compares gas and coal at varying methane leakage rates. We find that very small methane leakage rates from gas systems rival coal's greenhouse gas emissions," said Deborah Gordon, co-author of the analysis and a senior principal at the environmental group RMI, formerly Rocky Mountain Institute. Scientists from NASA, Harvard University and Duke University also contributed to the paper.
…
JULY 14, 20232:21 PM ET

The natural gas production and supply system leaks the powerful greenhouse gas methane during drilling, fracking, processing and transport.
Meredith Miotke for NPR
Natural gas has long been considered a more climate-friendly alternative to coal, as gas-fired power plants generally release less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than their coal-fired counterparts. But a new study finds that when the full impact of the industry is taken into account, natural gas could contribute as much as coal to climate change.
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. A new peer-reviewed analysis in the journal Environmental Research Letters finds that when even small amounts of methane escape from natural gas wells, production facilities and pipelines, it can drive up the industry's emissions to equal the effects of coal.
Recent studies have found much higher rates of leakage from natural gas infrastructure than previously known. Researchers wanted to understand the impact of those leaks.
"This analysis compares gas and coal at varying methane leakage rates. We find that very small methane leakage rates from gas systems rival coal's greenhouse gas emissions," said Deborah Gordon, co-author of the analysis and a senior principal at the environmental group RMI, formerly Rocky Mountain Institute. Scientists from NASA, Harvard University and Duke University also contributed to the paper.
…
OKIsItJustMe
(21,734 posts)6. China is rapidly taking global renewable capacity expansion to another level
https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2024/electricity#abstract
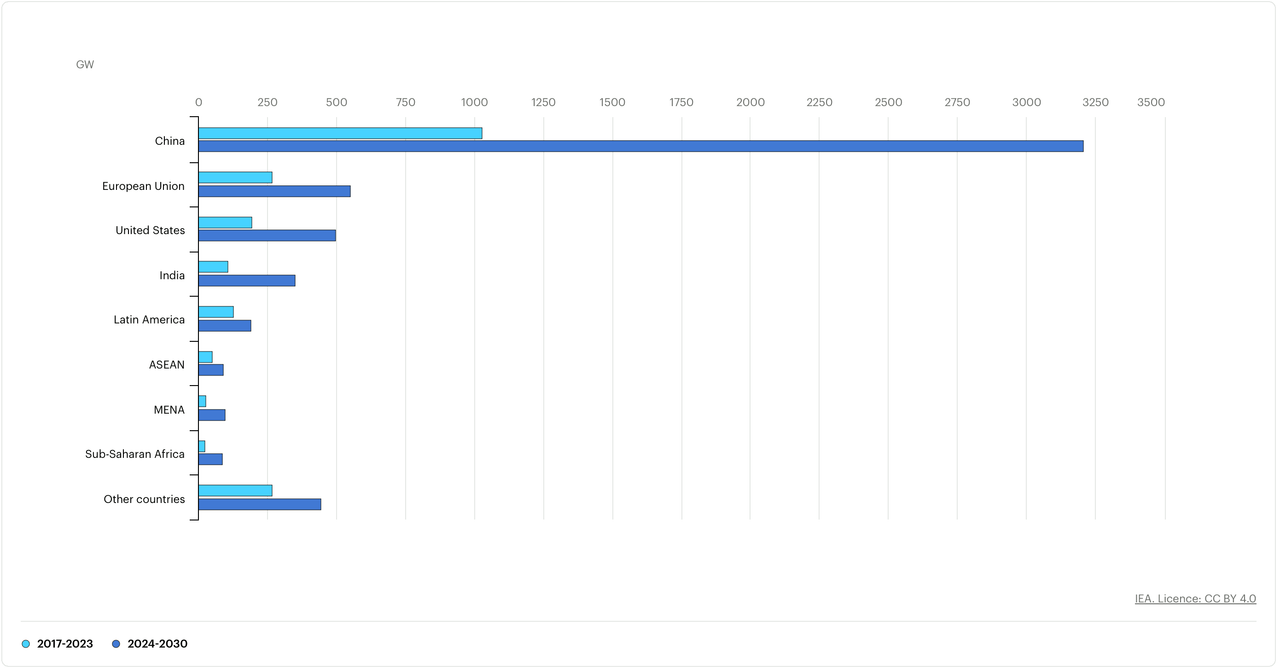
China already has more renewables than the USofA will have in 2030.
…
China is rapidly taking global renewable capacity expansion to another level
Over 2024-2030, China is expected to install 3 207 GW of new renewable electricity capacity, more than tripling growth of 2017-2023. Since 2015, China’s share in global annual capacity additions has been increasing and is expected to reach almost 60% in 2030. At the end of the forecast period, the country is expected to have at least half of the world’s cumulative renewable electricity capacity, doubling its share of the last decade. The Chinese government’s Net Zero by 2060 target, supported by incentives under the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025), and the ample availability of locally manufactured equipment and low-cost financing, stimulate the country’s renewable power expansion over the forecast period.
The European Union remains the second-largest growth market after China, with annual additions continuing to increase through 2030 at a faster pace than before. Member countries recently submitted their draft national plans to achieve the new overall EU target. For renewable electricity, their ambitions are in line with the overall EU goal, but they lack ambition for other sectors, including transport, industry and buildings. Renewable energy auctions, corporate PPAs and incentives stimulating distributed solar PV will continue to spur capacity growth in the next six years, doubling the bloc’s previous achievements.
…
https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/renewable-electricity-capacity-growth-by-country-region-main-case-2017-2030
China is rapidly taking global renewable capacity expansion to another level
Over 2024-2030, China is expected to install 3 207 GW of new renewable electricity capacity, more than tripling growth of 2017-2023. Since 2015, China’s share in global annual capacity additions has been increasing and is expected to reach almost 60% in 2030. At the end of the forecast period, the country is expected to have at least half of the world’s cumulative renewable electricity capacity, doubling its share of the last decade. The Chinese government’s Net Zero by 2060 target, supported by incentives under the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025), and the ample availability of locally manufactured equipment and low-cost financing, stimulate the country’s renewable power expansion over the forecast period.
The European Union remains the second-largest growth market after China, with annual additions continuing to increase through 2030 at a faster pace than before. Member countries recently submitted their draft national plans to achieve the new overall EU target. For renewable electricity, their ambitions are in line with the overall EU goal, but they lack ambition for other sectors, including transport, industry and buildings. Renewable energy auctions, corporate PPAs and incentives stimulating distributed solar PV will continue to spur capacity growth in the next six years, doubling the bloc’s previous achievements.
…

China already has more renewables than the USofA will have in 2030.