Environment & Energy
Showing Original Post only (View all)Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to DME, Tradeoff Between Hydrogen and Water as Chemical Reductant. [View all]
The paper I'll briefly discuss in this post is this one: Thermodynamic and Economic Assessments of Electrochemical CO2 Conversion to Dimethyl Ether: Trade-off between Hydrogen Gas and Water Vapor as a Proton Source, Brenden M. Arndt, Bryan Willson, and Mohammadreza Nazemi Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2024 63 (33), 14582-14589.
Let me begin with a couple of caveats.
The first is that while it is encouraging to see recent developments in the scientific literature focused on addressing the existing reality of extreme global heating - DME, a form of stored energy, as opposed to primary energy, is one of the most important to my mind - anything we do now or develop now, falls under the rubric of "too little, too late." This includes two recent papers in this journal - in which I'm behind in my reading - relating to the reprocessing of used nuclear fuels, specifically those to recover valuable lanthanide fission products, radiocerium, and radioeuropium from them. (I may try to find time to cover these papers.)
The second caveat is that electrochemical means of chemical production should always be regarded with suspicion because of two issues, the first being that electricity is overwhelmingly produced on this planet by combustion, the destruction of major river systems for hydroelectricity notwithstanding, as well as clean nuclear electricity, which has been prevented from doing what it might have done because of fear and ignorance. The second point is that electricity is thermodynamically degraded far beyond its primary energy sources. There are circumstances wherein electricity production could be utilized to minimize exergy destruction (although exergy destruction can never be prevented per the 2nd law of thermodynamics) via the use of heat networks in a nuclear powered process intensification systems, whereupon electricity would be a side product. This said, as I often note, could is a very different word that is. Despite all the lies we tell ourselves in denialist hype about the useless solar and wind industries, electricity is dirty, and thus all electrochemical processes are dirty.
This said, DME is a wonder fuel, an easily liquified gas (which can be thus utilized in heat pumps and as a refrigerant) that can replace all fuel uses associated with dangerous fossil fuels, fuels for internal combustion engines, natural gas, LPG, even, perhaps, jet fuel. It can be made by the dehydration of methanol, itself made from the catalytic hydrogenation of CO2; it should be noted that catalysts are known for the direct hydrogenation of CO2 to DME. Both types of hydrogenation are extremely exothermic; they generate heat, but they render the dangerous industrial gas hydrogen into a safe form. The critical temperature of DME is higher than the boiling point of water; the critical temperature of hydrogen is lower than the freezing point of methane.
An additional third caveat is that the paper posits that so called "renewable energy" will be the source of the electricity for the process, with this particular fantasy, even if soaking up uselessly vast sums of money, trillions of dollars, has proved trivial and useless in arresting the extreme global heating now observed. One does need to make grant applications to get things funded, and the religious faith that the reactionary scheme to make our energy supplies return, as was the case in the 19th century, to dependence on weather is a pernicious myth that remains hard to kill.
The paper does make reference to the danger of hydrogen, the consumer use of which is promoted for marketing purposes by the fossil fuel industry, which is why it is worthwhile, in an electrochemical process, to consider water as a proton source.
From the introduction:
Recycling CO2 emissions through electrolysis offers a viable solution that can create a circular carbon economy and a pathway to generate renewable carbon-based fuels. (1−3) Electrolysis for industrial applications has been extensively studied for hydrogen (H2) production. (4−6) Hydrogen gas has a superior energy density by mass but is quite volatile, leading to cost-prohibitive transportation due to its inherent danger. (7) Inspired by water electrolysis, the electroreduction of CO2 can produce diverse hydrocarbons and intermediates that can be used in transportation and industry. Adopting sustainable pathways to generate fuels and chemicals necessitates detailed analyses of the costs and energy associated with these new processes. Prior work on techno-economic assessments (TEA) of the CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) primarily focused on producing carbon monoxide (CO), formic acid (HCOOH), methane (CH4), ethylene (C2H4), and ethanol (C2H5OH). (8−16) All products have been shown that can be generated via the electrochemical CO2RR on transition metals such as silver (Ag), gold (Au), nickel (Ni), and copper (Cu). Here, we study electrochemical CO2RR to dimethyl ether (DME) from the direct route or intermediates. The common intermediates in the electrochemical CO2RR considered in this study are CO, HCOOH, and methanol (MeOH). The results are also compared with those of liquefied propane gas (LPG) and renewable natural gas (RNG).
CO2RR to CO is a pathway that has been extensively studied and has shown promising results for industrial production. A wide range of catalysts has been tested and has shown great selectivity toward CO, including surface additive Ag, Ni, and porous Au catalysts. (17−20) In particular, it has been shown using Ni coordination systems improves impurity tolerances on single-atom catalysts (SACs), which favors commercial applications due to impure gas streams. (21) This has also been shown to achieve high selectivities (greater than 95% Faradaic efficiencies (FE)) at high current densities (500 mA/cm2). In a tandem electrocatalytic CO2RR, low energy requirements reaction intermediates, such as CO and HCOOH (2 electron transfer processes), could be leveraged to produce more complex carbon-containing fuels. In addition, HCOOH is a viable hydrogen carrier and has been shown to be a potential fuel itself. (22,23) The electrochemical CO2RR to HCOOH occurs at relatively low cell voltages (1.5 V versus the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE)), at current densities as high as 200 mAcm–2. (24) This reaction is fully realized in acidic media (pH less than 1), which can negatively affect the mechanical behavior of metal catalysts due to corrosion. Formate (HCOO–) is another viable option that can be fully realized under alkaline conditions. This has been shown on cuprous oxide (Cu2O) catalysts with over 75% Faradaic efficiencies in H-cells. (25) Electrochemical CO2RR to MeOH is an evolving topic of interest as methanol is considered to be a viable fuel alternative and additive. (26) Additionally, methanol dehydration will result in the generation of DME, which is an excellent candidate for replacing diesel fuel in engines. DME has a higher cetane number, resulting in higher engine combustibility than diesel, coupled with no carbon-to-carbon bonds and 34.8% oxygen content, leading to virtually no particulate matter (PM) when combusted. (27) DME has a lower energy density than diesel (27.6 MJ/kg compared to 42.6 MJ/kg for diesel), requiring an engine double the size to achieve the same fuel economy as diesel.
It is important to draw a distinction between "Faradaic efficiency" and "Thermodynamic Efficiency." The former refers to the percentage of electrons that actually result in the production of the desired product. The latter refers to the exergy destruction involved in the process, which can never be zero.
Some graphics from the paper:
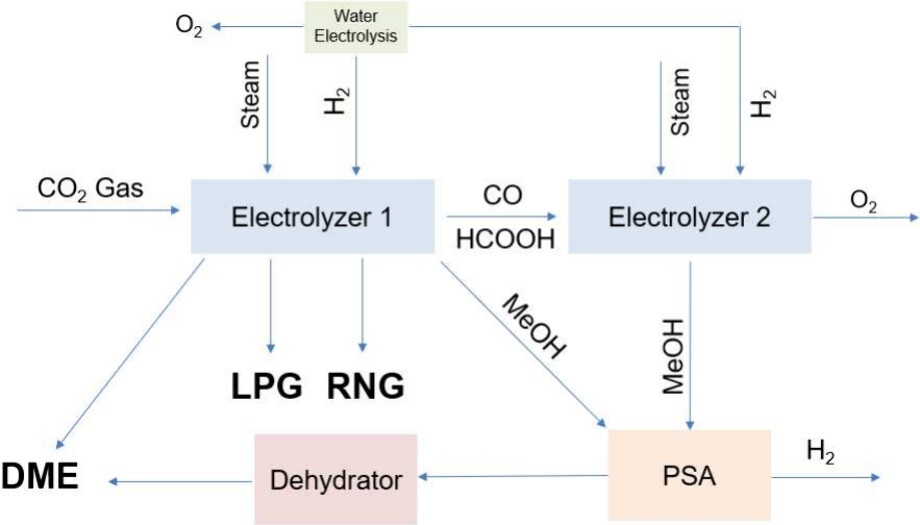
The caption:
aThere are various direct and multistep pathways that require different energies, impacting OPEX and CAPEX of the electrochemical fuel production system.
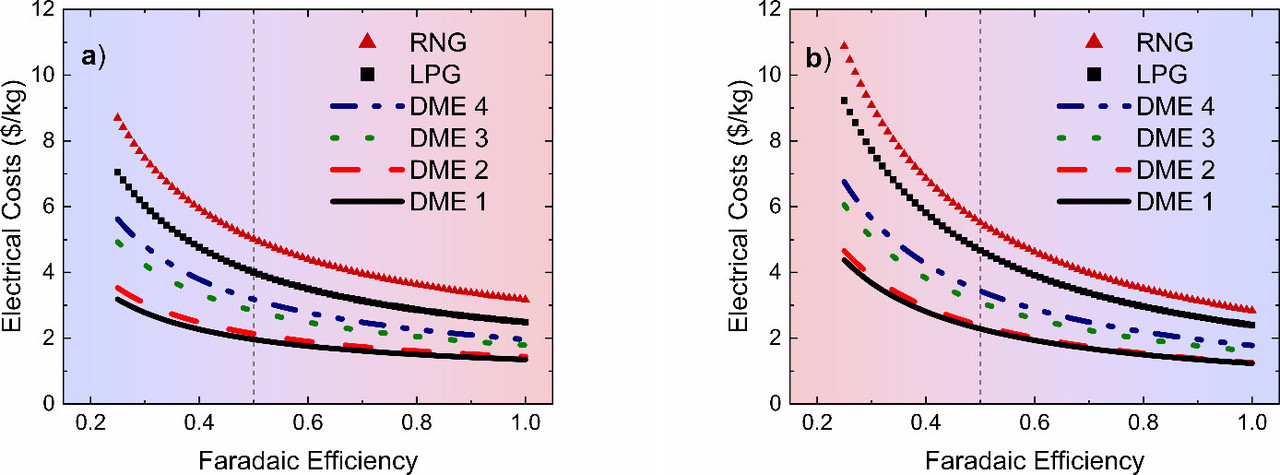
The caption:
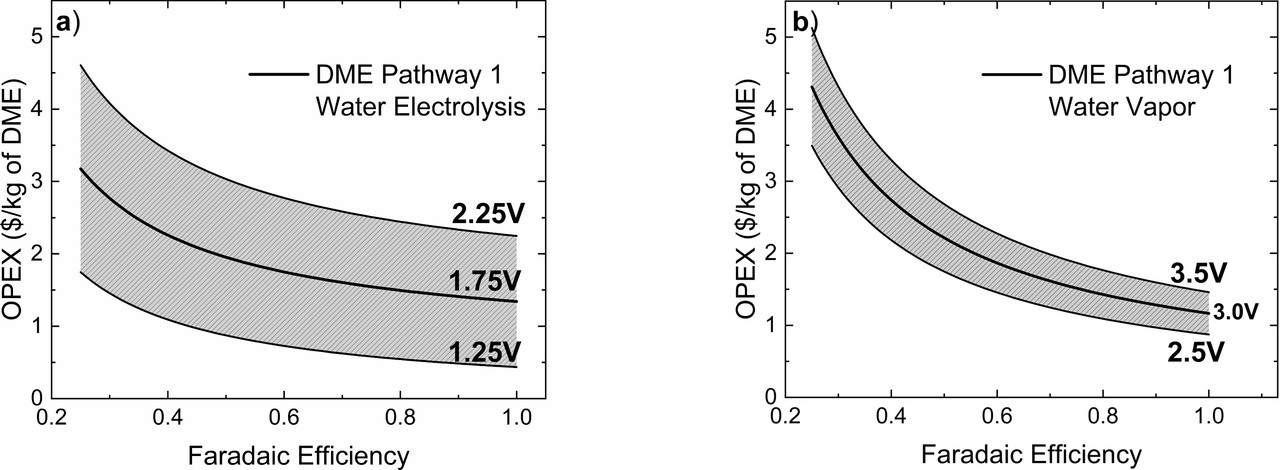
The caption:
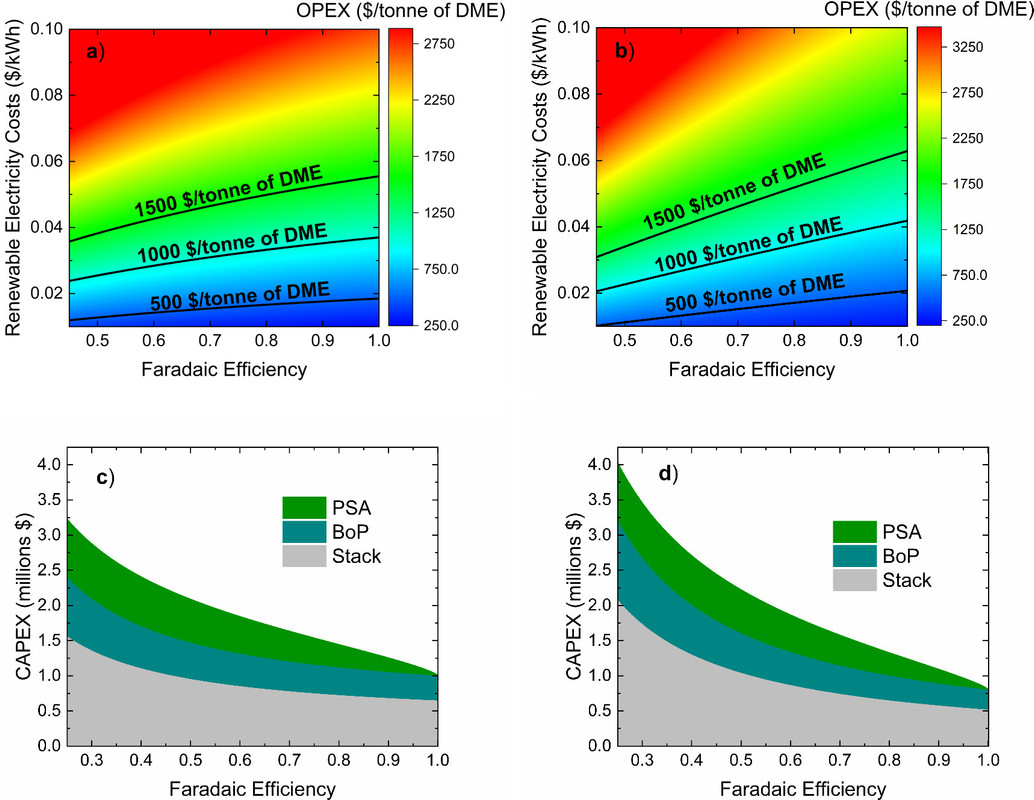
The caption:
I personally find the claim that a $0.02/kWh is feasible to be nonsensical, especially for so called 'renewable energy" whose redundancy costs are never acknowledged but are buried, but who cares what I think? In a process intensified systems with a heat network, however, it is possible, indeed desirable, to produce electricity in far excess of grid demand continuously and reliably, and divert the excesses to be utilized in industrial systems when grid demand is low and grid prices are too low to provide profitable sale, and sell it to the grid when demand is high, and thus grid prices are high. Under these circumstances, the industrial product costs will recover the OPEX costs of the electrical generation system. This has historically been practiced by the Kaiser Aluminum plants in the American Northwest which operated on hydroelectricity produced by the ecological destruction of river systems in that area.
I also note that the heat required for steam electrolysis is not conveniently available without raising exergy destruction thermodynamic and economic costs from so called "renewable energy" - wind and solar - but it is available cheaply from clean nuclear energy, with the added advantage of reducing the need for cooling.
Have a pleasant weekend.