Last edited Tue Oct 29, 2024, 08:54 PM - Edit history (1)
https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=55960MARCH 27, 2023
Renewable generation surpassed coal and nuclear in the U.S. electric power sector in 2022
 Data source
Data source: U.S. Energy Information Administration,
Electricity Data Browser
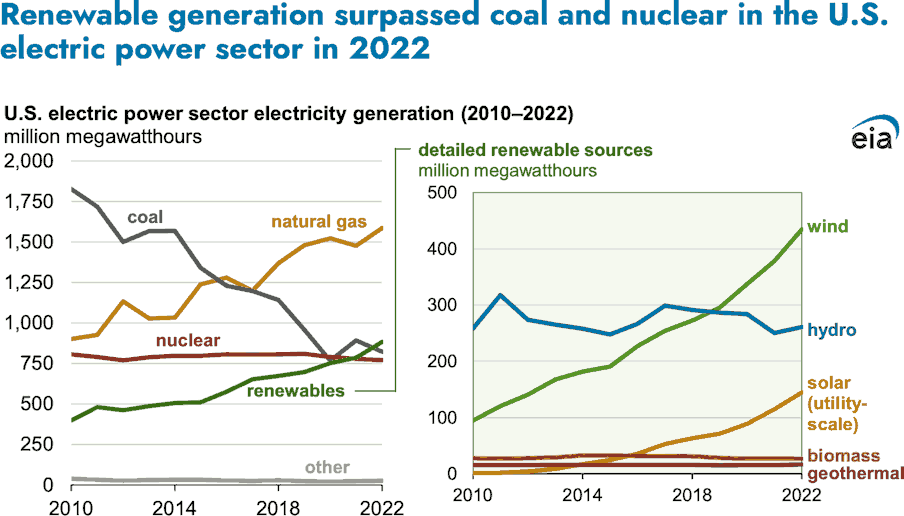
Last year, the U.S. electric power sector produced 4,090 million megawatthours (MWh) of electric power. In 2022, generation from renewable sources—wind, solar, hydro, biomass, and geothermal—surpassed coal-fired generation in the electric power sector for the first time.
Renewable generation surpassed nuclear generation for the first time in 2021 and continued to provide more electricity than nuclear generation last year.
Natural gas remained the largest source of U.S. electricity generation, increasing from a 37% share of U.S. generation in 2021 to 39% in 2022. The share of coal-fired generation decreased from 23% in 2021 to 20% in 2022 as a number of coal-fired power plants retired and the remaining plants were used less. The share of nuclear generation decreased from 20% in 2021 to 19% in 2022, following the
Palisades nuclear power plant’s retirement in May 2022. The combined wind and solar share of total generation increased from 12% in 2021 to 14% in 2022. Hydropower generation remained unchanged, at 6%, in 2022. The shares for biomass and geothermal sources remained unchanged, at less than 1%.
Growth in wind and solar generating capacity drove the increase in wind and solar generation. Utility-scale solar capacity in the U.S. electric power sector increased from 61 gigawatts (GW) in 2021 to 71 GW in 2022, according to data from our
Electricity Power Monthly. Wind capacity grew from 133 GW in 2021 to 141 GW in 2022.
More
wind-generated power was produced in Texas than in any other state last year. Texas accounted for 26% of total U.S. wind generation last year, followed by Iowa (10%) and Oklahoma (9%). One of the
largest wind farms in the United States (nearly 1,000 megawatt capacity [MW]) came online in Oklahoma in 2022.
…
 = new reply since forum marked as read
= new reply since forum marked as read
